Blog
Comparing Harness Wires: Selecting the Optimal Option for Your Electrical Needs
In the world of electrical assembly and design, selecting the right harness wire is crucial for ensuring both efficiency and safety. Harness wires play a pivotal role in connecting different components within electrical systems, and their proper selection can greatly impact the performance and reliability of these systems.

With a variety of types available, including PVC, XLPE, and Teflon, each harness wire comes with its own set of characteristics tailored to specific applications. This blog will delve into the factors to consider when choosing harness wires, highlighting examples of different types as well as their advantages and limitations.
By understanding these nuances, you will be better equipped to make informed decisions that meet your electrical needs effectively.
Understanding the Basics of Harness Wires and Their Applications
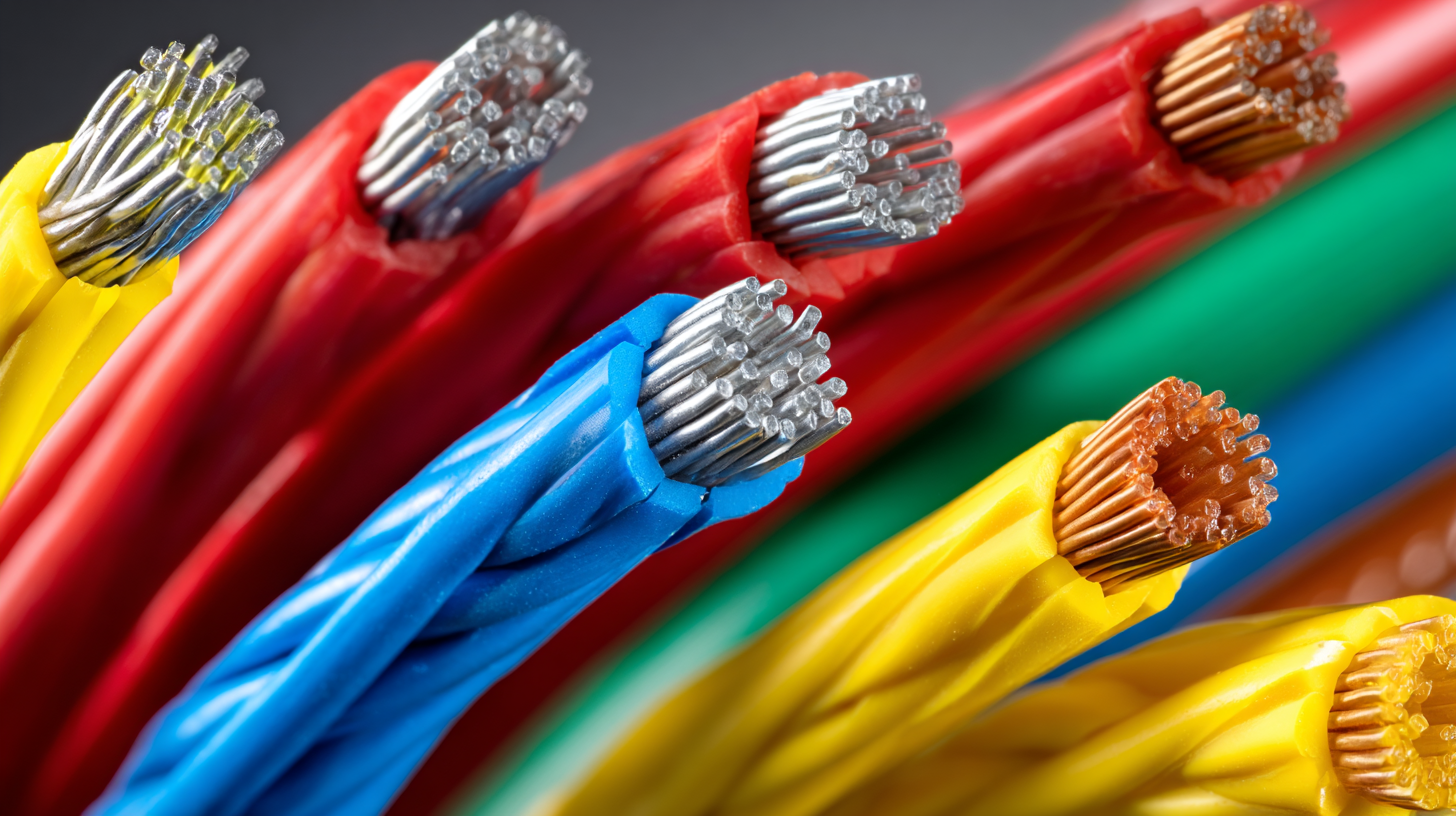 Harness wires are essential components in electrical systems, playing a crucial role in ensuring safe and efficient power distribution. These wires are typically bundled together to create a harness that streamlines installation and reduces the risk of wiring errors. Understanding the basics of harness wires involves recognizing their types, materials, and specific applications across various industries. Common wire types include stranded and solid wires, with stranded wires often favored for their flexibility and durability in dynamic environments.
Harness wires are essential components in electrical systems, playing a crucial role in ensuring safe and efficient power distribution. These wires are typically bundled together to create a harness that streamlines installation and reduces the risk of wiring errors. Understanding the basics of harness wires involves recognizing their types, materials, and specific applications across various industries. Common wire types include stranded and solid wires, with stranded wires often favored for their flexibility and durability in dynamic environments.
The applications of harness wires are vast, ranging from automotive to aerospace, telecommunications, and industrial machinery. In automotive applications, harness wires facilitate connections between different electrical systems, such as the engine management system, lighting, and infotainment features. For aerospace, harness wires must withstand extreme temperatures and vibrations, ensuring reliability in critical missions. Additionally, in industrial settings, harness wires are used to connect machinery and control systems, making efficiency and safety paramount. By selecting the right harness wires tailored to specific needs, users can significantly enhance performance and longevity in their electrical projects.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing the Right Harness Wire
Choosing the right harness wire is crucial for ensuring the efficiency and safety of your electrical systems. Several key factors should influence your decision-making process. First, consider the wire gauge, as it affects the amount of current the wire can carry. Thicker wires are suitable for high-voltage applications, while thinner wires are adequate for lower voltage systems.
Another important aspect to consider is the insulation material. Depending on your environment, you may need wire that can withstand extreme temperatures, moisture, or chemicals. For example, silicone insulation can handle high temperatures, while PVC is a versatile and cost-effective option for standard applications.
Tips: Always check the wire’s voltage rating and ensure it matches your system's requirements. Additionally, remember to consider the flexibility of the wire; stranded wires offer more bendability compared to solid wires, making them ideal for applications with frequent movement. Lastly, don’t overlook the importance of adherence to industry standards and regulations, as this can significantly affect the reliability and safety of your wiring system.
Comparative Analysis of Different Harness Wire Materials
When it comes to selecting harness wires for various electrical applications, understanding the materials available is crucial for optimizing performance and durability. Harness wires come in a range of materials, each offering unique properties that can significantly impact their suitability for specific tasks. For instance, copper remains a popular choice due to its excellent electrical conductivity and flexibility, making it ideal for most general applications. However, as the demand for enhanced performance grows, alternative materials like aluminum and stainless steel have become increasingly relevant.
Stainless steel, particularly grade 304, has garnered attention for its remarkable mechanical and physical properties, including its resistance to corrosion and high temperatures. This biocompatible material is especially advantageous in automotive wiring harnesses, where exposure to various environmental factors is a constant. In contrast, aluminum is lighter than copper, offering advantages in weight-sensitive applications, but it does not conduct electricity as well, which can be a limiting factor in certain uses. Conducting a comparative analysis of these harness wire materials enables manufacturers to make informed decisions tailored to their electrical needs, enhancing overall system reliability and performance.
Comparing Harness Wires: Selecting the Optimal Option for Your Electrical Needs
Best Practices for Harness Wire Installation and Maintenance
When it comes to harness wire installation and maintenance, following best practices is crucial for ensuring the longevity and reliability of your electrical systems. One essential tip is to organize your wires properly. Use cable ties or clips to keep wires separated and routed neatly. This not only prevents tangling but also reduces the risk of wear and tear due to friction.
Another important aspect is to perform regular inspections. Check for any signs of damage, such as fraying or discoloration, which can indicate deterioration. Addressing these issues promptly can save you from costly repairs down the line. Additionally, ensure that all connections are secure, as loose connections can lead to overheating and potential failures.
Lastly, when installing harness wires, pay attention to the environment in which they’ll be used. Consider factors like temperature and moisture, and choose materials that can withstand the conditions. Utilizing proper protective measures, such as sleeving or conduit, can greatly enhance the durability and performance of your harness wires.
Comparing Harness Wires: Selecting the Optimal Option for Your Electrical Needs
| Wire Type | Conductor Material | Insulation Type | Temperature Rating (°C) | Current Rating (A) | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC Insulated Wire | Copper | PVC | 75 | 20 | General Wiring |
| XLPE Insulated Wire | Aluminum | XLPE | 90 | 30 | Heavy Duty Applications |
| Silicone Insulated Wire | Copper | Silicone | 200 | 10 | High-Temperature Environments |
| Teflon Insulated Wire | Copper | Teflon | 200 | 15 | Chemical Resistance Applications |
| Rubber Insulated Wire | Copper | Rubber | 60 | 25 | Flexible Applications |
Environmental Considerations for Wire Selection in Electrical Projects
When selecting harness wires for electrical projects, it’s essential to consider the environmental impact alongside functionality and performance. The urgency to transition to alternative energy sources such as offshore wind farms and solar photovoltaic systems highlights the necessity for sustainable practices in our electrical frameworks. For instance, while offshore wind farms can significantly reduce carbon emissions, their installation poses challenges related to marine ecosystems, such as noise pollution and habitat disruption.

Tips: Choose wire materials that are recyclable and have a minimal environmental footprint. Consider insulation materials that are free from hazardous substances to ensure safety and sustainability.
Similarly, when assessing solar photovoltaic systems, one must be aware of the potential land, water, and pollution impacts. As the push for greener technologies intensifies, the wiring that connects these systems should align with sustainability goals.
Tips: Opt for wires that are certified for environmental safety and have been developed with eco-friendly practices. Regularly monitor the installation's ecological effects to adapt and mitigate potential impacts effectively.
Toll Free: (888) 802-2505
Phone: (256) 845-1255 or (256) 845-4493
Fax: (256) 845-1321 or (256) 845-4468
© 2025 Heritage Wire Harness, LLC
